What is Margin in Forex Trading?
Forex Trading, which involves buying and selling currencies, is one of the largest and most liquid financial markets in the world. For anyone looking to trade, understanding the concept of Forex margin is crucial. Margin in Forex plays a fundamental role in determining the amount of leverage a trader can use, which directly affects potential profit and loss. This comprehensive guide by OmegaFinex broker introduces you to the basics of margin, its types, how it works, and its implications in Forex trading.
What is Margin in Forex?
Margin in Forex is the amount of money a trader needs to open and maintain a position in the market. It acts as a required deposit to ensure that the trader can cover potential losses. Unlike a cost or fee, this amount is part of the trader’s equity set aside as a deposit.
Margin is important because it allows traders to open larger positions than they could with their capital alone. This is made possible through leverage. Leverage amplifies both potential profit and potential loss, making its management crucial for successful trading.
How Does Forex Margin Work?
When a trader opens a position, a certain amount of money from their account is set aside as the required margin. This amount is determined by the leverage ratio offered by the broker. For example, if a broker offers 100:1 leverage, the trader only needs to provide 1% of the total trade value as Forex margin.
Example:
- Trader’s Account Balance: $1,000
- Leverage: 100:1
- Trade Size: $100,000 (1 standard lot)
- Required Margin: $1,000 / 100 = $1,000
In this example, the trader can control a $100,000 position with just $1,000 of their money.
Types of Margin
Below are three types of Forex margin:
- Initial Margin: This is the amount required to open a new position. It is a percentage of the total trade size and varies depending on the broker and the currency pair being traded.
- Maintenance Margin: Also known as minimum margin in Forex, this is the minimum amount a trader must keep in their account to maintain an open position. If the account equity falls below this level, the trader will receive a margin call.
- Margin Call: A margin call occurs when the account equity falls below the required margin level. The broker will ask the trader to deposit additional funds or close positions to bring the account back to the required level. Failure to respond to a margin call can result in the broker closing positions to cover the margin shortfall.
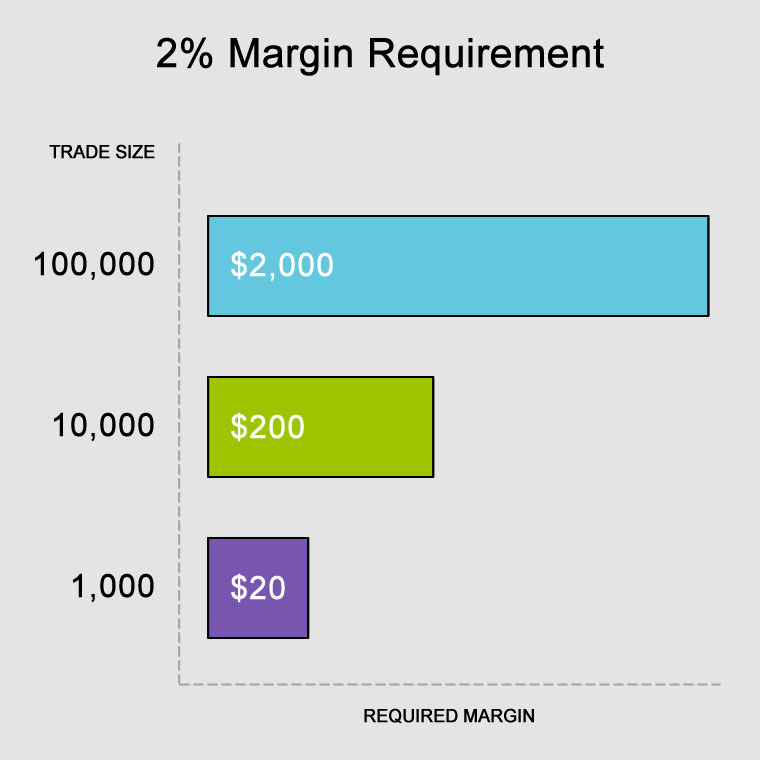
Calculating Forex Margin
The required margin in Forex is calculated using the following formula:
Required Margin = Trade Size / Leverage
Example:
- Trade Size: 1 standard lot (100,000 currency units)
- Leverage: 50:1
- Required Margin: 100,000 / 50 = 2,000 units of the base currency
Leverage and Margin
Leverage is the ratio of a trader’s funds to the size of the broker’s credit. It allows traders to control larger positions with a smaller amount of actual capital. The higher the leverage, the greater the potential profit or loss.
Leverage Ratios and Required Margin:
- 50:1 Leverage: 2% margin requirement
- 100:1 Leverage: 1% margin requirement
- 200:1 Leverage: 0.5% margin requirement
While leverage can amplify profits, it also increases risk. Traders should use it cautiously and fully understand the potential implications.
Risk Management and Margin in Forex
Effective risk management is crucial in Forex trading and technical analysis, especially when using leverage. Here are some strategies for managing related risks:
- Use Stop-Loss Orders: A stop-loss order automatically closes a position when it reaches a predetermined loss level. This helps limit potential losses and protect equity.
- Monitor Margin Levels: Regularly check margin levels to avoid margin calls in Forex. Ensure there is sufficient free margin in the account to cover potential losses.
- Diversify Positions: Avoid putting all your capital into a single trade. Diversify to spread risk across different currency pairs and consider trading in other markets such as stocks, cryptocurrencies, and indices.
- Educate Yourself: Continuously educate yourself on market conditions, trading strategies, and risk management techniques.
Margin on Different Trading Platforms
Different trading platforms and brokers have varying Forex margin requirements and policies. Understanding the specific terms and conditions of your chosen platform is essential. Here are some common types of margin policies:
- Fixed Margin: The margin requirement is fixed and does not change regardless of market conditions.
- Variable Margin: The margin requirement varies based on market conditions, such as volatility and liquidity.
- Tiered Margin: The margin requirement increases with the position size. Larger positions require higher margin deposits.
Example of Calculating Margin
Let’s consider an example to illustrate how Forex margin works in practice.
Example:
- Account Balance: $5,000
- Leverage: 100:1
- Currency Pair: EUR/USD
- Trade Size: 1 standard forex lot (100,000 units)
- EUR/USD Exchange Rate: 1.2000
Step-by-step Calculation:
1. Calculate the Trade Value:
Trade Value = Trade Size*Exchange Rate
100,000* 1.2000 = $120,000
2. Calculate the Required Margin in Forex:
Required Margin = Trade Value /Leverage
120,000/100 = $1,200
In this example, the trader needs $1,200 as margin to open a position worth $120,000.
Continuing from the above example, let’s assume the market moves against the trader, and the account equity falls below the required margin in Forex.
- Account Equity: $1,000
- Maintenance Margin Requirement: $1,200
Since the account equity ($1,000) is less than the required maintenance margin ($1,200), the trader will receive a margin call. They need to deposit additional funds or close positions to meet the margin requirement.
Advantages and Risks of Margin in Forex
lets consider the risks and advantages of margin trading in forex:
Advantages:
Amplified Profits: Leverage allows traders to control larger positions, potentially leading to higher profits in successful trades.
Increased Market Exposure: With Forex margin, traders can participate in more significant market movements without needing substantial capital.
Risks:
Amplified Losses: Just as leverage can amplify profits, it can also amplify losses. Traders can lose more than their initial deposit if the market moves against them.
Margin Calls: This can lead to the forced liquidation of positions, potentially at unfavorable prices.
Emotional Stress: The high risks involved in margin trading can lead to emotional stress and impulsive decision-making.
Best Practices for Margin Trading in Forex
To successfully navigate the challenges of margin trading, consider the following best practices:
- Understand Leverage: Fully understand leverage and its associated risks before using it.
- Use Risk Management Tools: Use stop-loss orders, take-profit orders, and other risk management tools to protect your capital.
- Start Small: Begin with smaller positions and minimum balance for forex, gradually increasing as you gain experience and confidence.
- Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date with market news, economic indicators, and geopolitical events that can affect currency prices. Using an economic calendar is an effective way to stay informed.
- Maintain Sufficient Capital: Ensure you have enough capital to cover the required margin in Forex and withstand potential losses.
Conclusion
Margin in Forex is a fundamental concept that allows traders to control larger positions with a smaller amount of capital. While it offers the potential for higher profits, it also comes with increased risk. Understanding how it works, managing leverage effectively, and employing appropriate risk management strategies are essential for successful Forex trading.
By mastering the principles of Forex margin and leverage, traders can enhance their trading performance and navigate the Forex market with greater confidence and control. Remember, continuous education and practice are key to excelling in this form of trading and achieving long-term success in the Forex market.