What is Slippage in Forex?
Forex trading is a dynamic and fast-paced market where traders aim to profit from currency exchange rate fluctuations. One of the key concepts traders need to understand to navigate this market effectively is “Forex slippage.” Slippage is a phenomenon that can impact trade execution, and understanding it is crucial for both new and experienced traders. This article from OmegaFinex explains what slippage in Forex is, why it happens, and how traders can manage it to minimize its effects.
What is Slippage in Forex?
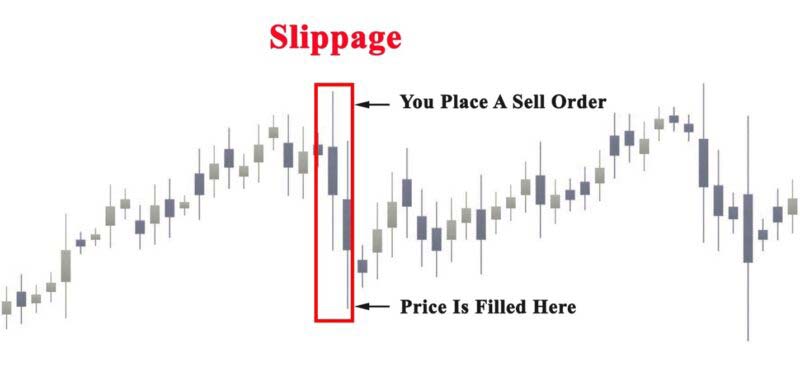
Slippage occurs when there is a difference between the expected price of a trade and the actual price at which the trade is executed. This can happen in any financial market, including Forex, stocks, indices, cryptocurrencies, and metals trading, but it is especially common in Forex due to its high volatility and liquidity.
For example, if a trader places a buy order for EUR/USD at 1.2000, but the order is executed at 1.2005, the slippage is 5 pips. Similarly, if a trader places a sell order at 1.2000 but the order is executed at 1.1995, the slippage is also 5 pips.
Types of Forex Slippage
Slippage in Forex can be positive, negative, or neutral:
- Positive Slippage: Occurs when the execution price is better than the expected price. For example, if you place a buy order at 1.2000 and it gets executed at 1.1995, you experience positive slippage.
- Negative Slippage: Happens when the execution price is worse than the expected price. For instance, if you place a sell order at 1.2000 and it gets executed at 1.2005, you experience negative slippage in forex.
- Neutral Slippage: Occurs when the execution price is exactly the expected price. This is often the ideal scenario for traders.
Why Does Slippage Happen?
Several factors contribute to slippage in Forex:
Market Volatility: High volatility often leads to rapid price changes, making it difficult to execute orders at the desired price. Economic news releases, geopolitical events, and unexpected announcements can all increase volatility.
Liquidity: Liquidity refers to the availability of buyers and sellers in the market. In highly liquid markets, orders are more likely to be filled at the expected price. However, in less liquid markets, large orders can cause significant price changes, leading to Forex slippage.
Order Type: The type of order placed can affect the likelihood of slippage. Market orders, which are executed immediately at the best available price, are more prone to slippage compared to limit orders, which are executed at a specified price or better.
Broker Execution Speed: The speed at which a broker executes orders can impact slippage in Forex. Faster execution generally results in less slippage, while slower execution can lead to a larger difference between the expected and actual prices.
Impact of Slippage on Trades
Forex slippage can have both positive and negative effects on trades. Positive slippage can increase profits by providing a better entry or exit price than expected. Conversely, negative slippage can reduce profits or increase losses due to a less favorable execution price.
For example, consider a trader who places a buy order for EUR/USD at 1.2000 with a stop loss at 1.1950. If the order is executed at 1.2005 due to slippage, the stop loss effectively moves to 1.1955, increasing potential losses. Conversely, if the order is executed at 1.1995, the stop loss effectively moves to 1.1945, potentially reducing the loss.
Strategies for Managing Slippage in Forex
While it is impossible to eliminate forex slippage entirely, traders can employ several strategies to manage and minimize its impact:
- Use Limit Orders: Limit orders allow traders to specify the price at which they are willing to buy or sell. Unlike market orders, which are executed at the best available price, limit orders are only executed at the specified price or better. This can help avoid negative slippage, though it may result in missed trading opportunities if the market does not reach the specified price.
- Trade During High Liquidity Periods: Trading during high liquidity times, such as the overlap of major sessions (e.g., London-New York overlap), can reduce the likelihood of slippage in Forex. High liquidity ensures there are enough buyers and sellers to complete orders at the desired price.
- Avoid Trading During Major News Releases: Major economic news releases can cause significant market volatility and increase the likelihood of slippage. By avoiding trading during these times, traders can reduce the risk of experiencing Forex slippage.
- Choose a Reliable Broker: The choice of broker can significantly impact the level of Forex slippage experienced. Reputable brokers with fast and reliable execution systems are less likely to cause slippage. Additionally, some brokers offer guaranteed stop-loss orders, which can help limit losses due to slippage.
- Use Slippage Control Tools: Some trading platforms offer slippage control tools that allow traders to set the maximum allowable slippage in Forex. If the slippage exceeds this amount, the order will not be executed. This can help protect traders from excessive slippage.
Calculating and Analyzing Slippage
Understanding and analyzing slippage in Forex is essential for developing effective trading strategies. Traders can calculate slippage by comparing the expected price of an order with the actual execution price. The formula is as follows:
Slippage = Actual Execution Price – Expected Price
For example, if a trader expects to buy EUR/USD at 1.2000 but the order is executed at 1.2003, the Forex slippage is:
Slippage = 1.2003 – 1.2000 = 0.0003 or 3 pips
By tracking slippage over a series of trades, traders can gain insight into the conditions that lead to slippage and adjust their strategies accordingly. For example, if a trader consistently experiences Forex slippage at certain times of the day or when trading specific currency pairs, they might avoid trading under those conditions.
The Role of Technology in Reducing Slippage in Forex
Advancements in technology have significantly reduced slippage in Forex. High-frequency trading (HFT) algorithms, direct market access (DMA) platforms, and low-latency execution systems all contribute to faster and more accurate order execution.
High-Frequency Trading (HFT): HFT algorithms execute a large number of orders at very high speeds, often in fractions of a second. This can reduce Forex slippage by taking advantage of small price differences and ensuring quick order completion.
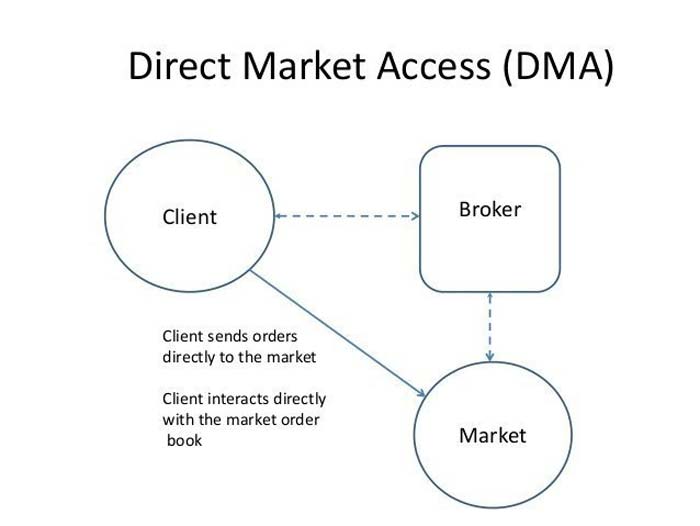
Direct Market Access (DMA): DMA platforms provide traders with direct access to exchange order books, allowing them to see real-time market data and place orders directly. This can reduce the time needed for order execution and minimize slippage in Forex.
Low-Latency Execution Systems: Low-latency execution systems are designed to minimize the delay between placing and executing orders. By reducing latency, these systems can help ensure that orders are executed at the expected price, thereby reducing the likelihood of Forex slippage.
Examples of Slippage in Trading
To illustrate the impact of slippage, consider the following real-world scenarios:
- Scenario 1: Positive Slippage: A trader places a buy order for GBP/USD at 1.3000 during a high liquidity period. The order is executed at 1.2998, resulting in a positive slippage of 2 pips. The trader benefits from a better entry price, potentially increasing their profit.
- Scenario 2: Negative Slippage: A trader places a sell order for USD/JPY at 110.00 during a major economic news release. Due to increased volatility, the order is executed at 110.05, resulting in a negative slippage of 5 pips. The trader incurs a larger loss than expected.
- Scenario 3: Neutral Slippage: A trader places a limit order to buy AUD/USD at 0.7500. The market reaches the specified price, and the order is executed exactly at 0.7500, resulting in neutral slippage in Forex. The trader’s order is completed at the expected price.
Conclusion
Slippage in Forex is an inherent aspect of trading that can have both positive and negative effects on trade outcomes. By understanding the factors contributing to slippage and employing strategies to manage it, traders can minimize its impact and improve their trading performance.
Effective methods include using limit orders, trading during high liquidity periods, avoiding major news releases, choosing a reliable broker, and leveraging technology. By being aware and proactive, traders can navigate the complexities of slippage and increase their chances of success in the Forex market.