What is Spread in Forex? 0 to 100 About Forex Spread
The dynamic Forex market attracts traders of all levels, from beginners to experienced professionals, due to its high liquidity, 24-hour trading, and significant profit potential. One essential concept every trader needs to understand for Forex trading and technical analysis is the forex spread. This article by OmegaFinex explains the concept of spread in Forex, covering its definition, types, influencing factors, and effective management strategies.
What is Spread in Forex?
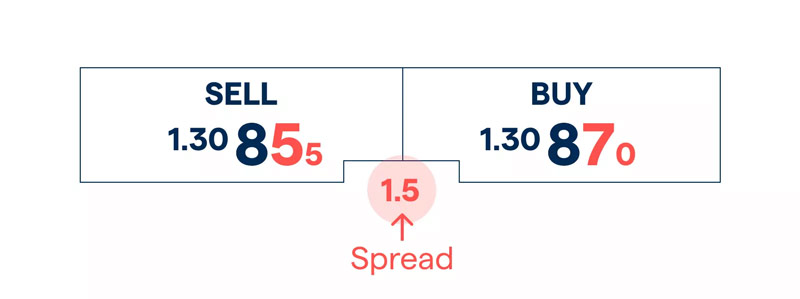
The spread in Forex is the difference between the bid price and the ask price of a currency pair. The bid price is the highest price a buyer is willing to pay for a currency, while the ask price is the lowest price a seller is willing to accept. This concept represents the cost of trading and is usually measured in pips, which is the smallest price movement in Forex trading, typically equivalent to 0.0001 for most currency pairs.
Types of Forex Spread
There are two main types of Forex spreads: fixed and variable (or floating).
- Fixed Spreads: Fixed spreads remain constant regardless of market conditions. They are set by brokers and do not change based on market volatility or liquidity. Fixed spreads provide predictability, making it easier for traders to calculate trading costs and manage their budget. However, during low market volatility, fixed spreads can be higher than variable spreads, potentially increasing trading costs.
- Variable Spreads: Variable spreads fluctuate based on market conditions. They widen during high volatility periods and narrow during low volatility periods. Variable spreads can be lower than fixed spreads in stable market conditions, reducing trading costs. However, their unpredictability can make estimating trading costs challenging, especially during market volatility.
Factors Influencing Spread in Forex
Several factors affect the spread in Forex:
Market Liquidity: Higher liquidity usually leads to lower spreads because there are more buyers and sellers in the market. Major currency pairs like EUR/USD, GBP/USD, and USD/JPY typically have tighter spreads due to high trading volumes.
Market Volatility: Increased volatility often results in wider Forex spreads as brokers account for the higher risk of price fluctuations. News events, economic data releases, and geopolitical developments can all contribute to market volatility.
Trading Session: The time of day can impact spreads. For example, spread in Forex tend to narrow during the overlap of the London and New York sessions due to increased trading activity. Conversely, spreads may widen during the Asian session when trading volumes are lower.
Broker Type: Different brokers offer different Forex spreads based on their trading models. Market makers usually offer fixed spreads, while ECN brokers provide variable spreads. ECN brokers give access to the interbank market, where spreads may be lower but commissions are charged per trade.
Currency Pair: Major currency pairs generally have lower spreads due to higher liquidity, compared to exotic currency pairs. Exotic pairs, involving emerging market currencies, often have wider spreads due to lower trading volumes and higher risk.
Strategies for Managing Forex Spread
Effectively managing spread in Forex is crucial for traders aiming to maximize their profits. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Choosing the Right Broker: Selecting a broker that offers competitive spreads is essential. Traders should compare spreads across different brokers and choose one that aligns with their trading style and budget. ECN brokers can be beneficial for traders seeking lower spreads, but it’s important to consider any additional commissions.
- Trading During High Liquidity Periods: Trading during high liquidity periods, such as the overlap of major trading sessions, can help reduce costs. Avoiding trading during low liquidity periods, like weekends or holidays, can prevent facing wider spreads.
- Avoiding High-Volatility News Events: Economic data releases and major news events can cause significant market volatility, leading to wider spreads. Traders should consider avoiding trading during these times or use appropriate risk management strategies, such as setting wider stop-loss orders.
- Using Limit Orders: Limit orders allow traders to set a specific price at which they want to buy or sell a currency pair. This can help avoid paying higher spreads during volatile market conditions. By using limit orders, traders can wait for the market to reach their desired price instead of accepting the current market price with a wider spread in Forex.
- Monitoring and Adjusting Trading Strategies: Regularly monitoring spreads and adjusting trading strategies based on market conditions can help manage costs. Traders should stay informed about factors that influence spread in Forex and be flexible in adapting their strategies accordingly.
Impact of Spread on Trading Performance
Spread in Forex directly affects the final price a trader pays and influences entry and exit points in a trade. Here’s how:
Cost of Entry and Exit: Spread represents the cost of entering and exiting a trade. A wider spread increases this cost, reducing potential profits or increasing potential losses. For example, if the EUR/USD spread is 2 pips, a trader must overcome this cost before making a profit.
Scalping Strategies: Scalping involves making multiple small trades to capture small price movements. Since spread is a significant cost in scalping, traders using this strategy prefer lower spreads. High spreads can make scalping unprofitable, as costs might exceed the gains from small price movements.
Long-Term Trading: Long-term traders are less affected by spread because they aim for larger price movements over extended periods. However, managing spreads is still important to ensure overall profitability.
Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Levels: Wider spreads can affect the placement of stop-loss and take-profit levels. Traders need to consider the spread when setting these levels to avoid premature stop-outs or missed profit targets. Ensuring these levels are set beyond the spread can help maintain effective risk management.
Summary
Understanding and managing spread in Forex is essential for successful trading. Spread represents the cost of trading and can significantly impact profitability. By understanding the types of spreads, the factors influencing them, and strategies for managing them, traders can make informed decisions and enhance their trading performance.
Choosing the right broker, trading during high liquidity periods, avoiding high-volatility news events, using limit orders, and regularly adjusting trading strategies are effective ways to manage Forex spread. By incorporating these strategies into their trading plans, traders can minimize costs, optimize their entry and exit points, and ultimately improve their overall success in the Forex market.
In the ever-evolving world of Forex trading, staying informed and adaptable is key. As traders gain more experience and knowledge, they can refine their approaches to managing spread, ensuring it remains a vital aspect of their journey towards profitability and sustained success.