What Are Currency Pairs? Types of Forex Pairs
The core concept in forex trading is currency pairs. This comprehensive article from Omega Finex broker discusses what forex pairs are, how they work, introduces the types of currency pairs in forex, and teaches strategies for effective trading of these pairs.
What is a Forex Currency Pair?
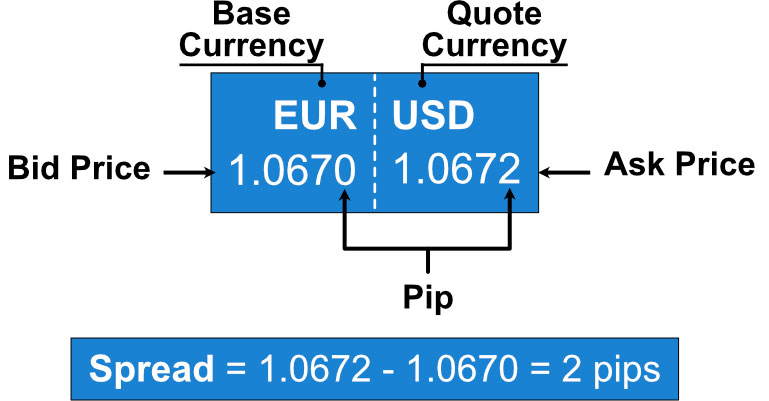
A currency pair is a quote of two different currencies, showing the value of one currency against the other. The first currency listed in a pair is called the base currency, while the second currency is known as the quote currency. A forex pair indicates how much of the quote currency is needed to buy one unit of the base currency.
For example, in the EUR/USD pair: EUR is the base currency, and USD is the quote currency. If the pair is quoted at 1.1200, it means that 1 Euro is equivalent to 1.1200 USD.
How Do Forex Pairs Work?
Forex trading involves buying one currency and simultaneously selling another. When you trade a currency pair, you are speculating on the value of the base currency relative to the quote currency. If you believe the base currency will strengthen against the quote currency, you buy the pair. Conversely, if you think the base currency will weaken against the quote currency, you sell the pair.
Example: EUR/USD = 1.1200. If you buy EUR/USD, you are buying Euros and selling Dollars. If the exchange rate rises to 1.1300, the Euro has strengthened against the Dollar. You can sell Euros at the higher rate for Dollars and make a profit.
Types of Currency Pairs in Forex
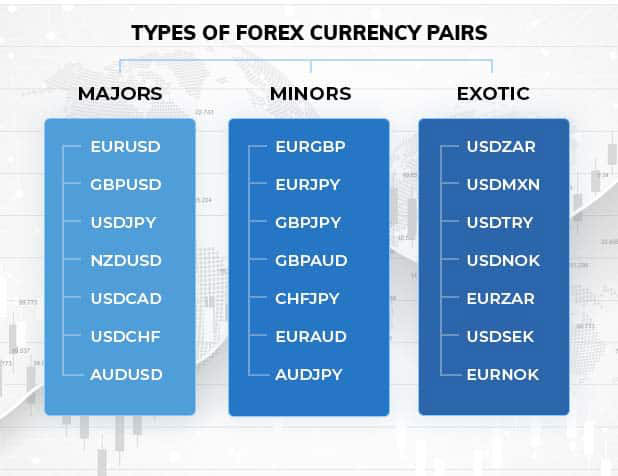
There are generally three types of currency pairs in forex: major pairs, minor pairs, and exotic pairs.
- Major Pairs: These are the most traded currency pairs in forex. They include the most stable and widely used currencies in the world. Major pairs always include the US Dollar (USD) as either the base or the quote currency. Examples: EUR/USD, USD/JPY, GBP/USD, USD/CHF, AUD/USD, USD/CAD, NZD/USD.
- Minor Pairs: Also known as cross-currency pairs, these do not include the US Dollar. These forex currency pairs involve trading major currencies against each other. Examples: EUR/GBP, EUR/AUD, GBP/JPY, CHF/JPY, NZD/JPY.
- Exotic Pairs: Exotic currency pairs consist of a major currency paired with the currency of a smaller or emerging economy. These forex pairs have less liquidity compared to major and minor pairs. Examples: USD/TRY (US Dollar/Turkish Lira), EUR/TRY (Euro/Turkish Lira), USD/HKD (US Dollar/Hong Kong Dollar), USD/ZAR (US Dollar/South African Rand).
Factors Influencing Pairs
Multiple factors impact the movement of forex currency pairs. Understanding these factors is crucial for making informed decisions.
Economic Indicators: The release of economic data, such as GDP growth, unemployment rates, inflation, and retail sales, can significantly influence a currency’s value. Strong economic data from a country usually strengthens its currency, while weak data can weaken it.
Interest Rates: Central banks influence currency values through interest rate policies. Higher interest rates attract foreign capital, leading to an increase in currency value. Conversely, lower interest rates can lead to a decrease in currency value.
Political Stability: Political events such as elections, government policies, and geopolitical tensions can cause forex currency pairs to fluctuate. Political stability generally supports a stronger currency, while instability can weaken it.
Market Sentiment: Trader perceptions and market sentiment can drive currency prices. Positive sentiment towards a currency can lead to increased buying, while negative sentiment can lead to selling.
Global Events: Events such as natural disasters, pandemics, and international conflicts can affect currency values. These events can cause uncertainty and volatility in the forex market.
How to Trade Different Forex Pairs
Trading forex pairs involves several steps, from selecting a pair to executing the trade and managing risk.
- Selecting a Currency Pair: Choose a forex currency pair based on your trading strategy, market analysis, and risk tolerance. Consider factors like liquidity, volatility, and trading hours when selecting a pair.
- Market Analysis: Use technical analysis, fundamental analysis, or a combination of both to analyze the market. Technical views involves studying price charts and using various technical indicators to identify trends and patterns. Fundamental analysis involves assessing economic data, news events, and market sentiment to predict currency movements.
- Developing a Trading Strategy: Create a trading strategy that suits your trading style and goals. Consider factors like entry and exit points, stop-loss and take-profit levels, and risk management.
- Executing the Trade: Execute the trade by placing an order with your broker. Depending on your trading strategy, you can place different types of orders, such as market orders, limit orders, and stop orders.
- Risk Management: Risk management is crucial in forex trading to protect your capital. Use stop-loss orders to limit potential losses and take-profit orders to lock in profits. Avoid excessive leverage and use appropriate position sizing to manage risk effectively.
Example of a Trading Strategy Using Currency Pairs
Here is an example of a trading strategy using forex currency pairs:
- Identify the Trend: Use the moving average crossover strategy to identify the trend. When the short-term moving average crosses above the long-term moving average, it indicates an uptrend (buy signal). When the short-term moving average crosses below the long-term moving average, it indicates a downtrend (sell signal).
- Confirm with Indicators: Confirm the trend using additional indicators like the Relative Strength Index (RSI) and the Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD). In an uptrend, the RSI should be above 50, and the MACD should show a bullish crossover. In a downtrend, the RSI should be below 50, and the MACD should show a bearish crossover.
- Enter the Trade: Enter a buy position in an uptrend when the price retraces to the short-term moving average and shows signs of bouncing. Enter a sell position in a downtrend when the price retraces to the short-term moving average and shows signs of falling.
- Set Stop-Loss and Take-Profit: Place a stop-loss order below the recent swing low in an uptrend or above the recent swing high in a downtrend. Set a take-profit order at a key resistance level in an uptrend or a key support level in a downtrend.
- Monitor the Trade: Continuously monitor the trade and adjust stop-loss and take-profit levels based on price movements and the identification of new support and resistance levels.
Common Forex Pairs for Trading
There are many commonly traded types of currency pairs. Here are some of the most popular ones along with their characteristics:
EUR/USD (Euro/US Dollar): The most traded forex pair in the world. It has very high liquidity and low, stable spreads. It is influenced by economic data from the Eurozone and the United States.
USD/JPY (US Dollar/Japanese Yen): Known for high liquidity and low spreads. It is influenced by economic data from the US and Japan and is often used as a safe haven currency pair during market uncertainty.
GBP/USD (British Pound/US Dollar): Highly liquid with moderate spreads. It is influenced by economic data from the UK and the US.
USD/CHF (US Dollar/Swiss Franc): Known for its safe haven status. It has high liquidity with moderate spreads and is influenced by economic data from the US and Switzerland.
AUD/USD (Australian Dollar/US Dollar): This pair is known for its commodity correlation, especially with gold and iron ore. It has high liquidity with moderate spreads and is influenced by economic data from Australia and the US.
USD/CAD (US Dollar/Canadian Dollar): Known for its correlation with oil prices. It has high liquidity with moderate spreads and is influenced by economic data from the US and Canada.
NZD/USD (New Zealand Dollar/US Dollar): Known for its commodity correlation, especially with dairy products. It has relatively good liquidity with slightly wider spreads and is influenced by economic data from New Zealand and the US.
Conclusion
Understanding forex pairs is essential for anyone looking to trade in the forex market. These pairs represent the value of one currency relative to another and are categorized into major, minor, and exotic pairs. Various factors, including economic indicators, interest rates, political stability, market sentiment, and global events, influence the movement of different types of currency pairs.