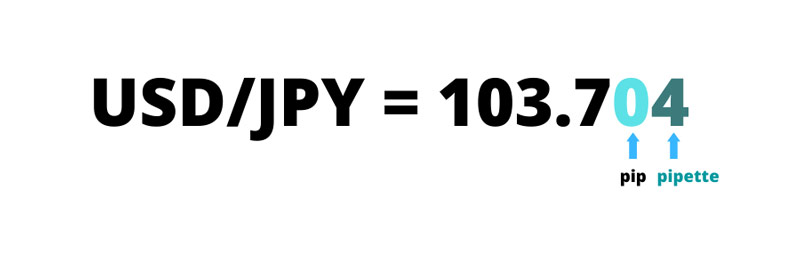The foreign exchange market, or forex, is the largest and most liquid financial market in the world, operating 24 hours a day, five days a week, with a daily trading volume exceeding $6 trillion. Given its vast size and complexity, understanding basic concepts is crucial for anyone looking to forex trading.
One of these fundamental concepts is the pip in forex. For any trader, even using minimum balance for forex trading , understanding the basic concept of a pip is essential, and this article from the OmegaFinex broker website will provide a complete explanation.
What is a Pip in Forex?
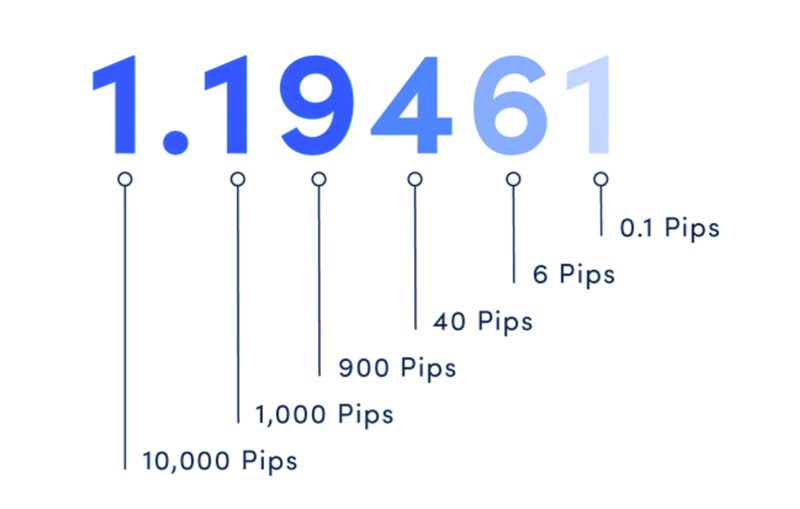
A forex pip, short for “percentage in point,” is a standardized unit of measurement for price movement in the forex market. It represents the smallest possible price change that a given exchange rate can make based on market conventions. For most currency pairs, a pip is the fourth decimal place (0.0001), while for pairs involving the Japanese yen, a forex pip is the second decimal place (0.01). Understanding pips is crucial for forex traders because they are the basis for calculating profit, loss, and risk.
Practically speaking, a pip in forex is used to express the change in value between two currencies. For example, if the EUR/USD exchange rate moves from 1.1050 to 1.1051, it has moved one pip in forex. This small unit of measurement allows traders to precisely quantify and compare price changes in currency pairs, providing a clear benchmark for assessing market movements. Since forex trading often involves significant amounts of money, even small changes measured in pips can lead to substantial financial consequences.
The value of a pip in forex can vary depending on the currency pair being traded, the trade size, and the exchange rate. For instance, when trading a standard lot (100,000 units) of EUR/USD at an exchange rate of 1.1050, one pip is worth approximately $10. This calculation is vital for traders to understand their potential profit or loss on any trade, enabling them to manage their positions effectively. By knowing the value of a pip, traders can better assess their risk and set appropriate stop-loss and profit target levels.
Moreover, forex pips are essential for executing various technical analysis strategies and risk management techniques. Traders use pips to determine the spread (the difference between the bid and ask price), to set stop-loss and profit target orders, and to calculate position size. For example, a trader might decide to risk 20 pips on a trade with the expectation of gaining 40 pips, thus creating a risk-to-reward ratio of 1:2. By mastering the concept of pip in forex, traders can make more informed decisions and improve their ability to achieve consistent profitability in the forex market.
Importance of Forex Pips
Pips are essential in forex trading because they quantify the price changes in currency pairs. Traders use forex pips to calculate the spread (the difference between the bid and ask price), set stop-loss and take-profit orders, and measure potential profits or losses. Understanding how to calculate and interpret pips is fundamental for effective risk management and strategy development.
Calculating Pip Value
Let’s explore how to calculate the value of a pip in forex:
Major Currency Pairs (e.g., EUR/USD, GBP/USD): For most pairs, one pip is equal to 0.0001. Example: If EUR/USD moves from 1.1050 to 1.1051, it has moved by one pip.
Japanese Yen Pairs (e.g., USD/JPY, EUR/JPY): For pairs involving the Japanese yen, one pip is equal to 0.01. Example: If USD/JPY moves from 110.10 to 110.11, it has moved by one pip in forex.
The value of a pip in forex depends on the currency pair being traded, the trade size, and the exchange rate. Here’s how to calculate the value of a pip:
Formula:
- For a Standard Lot (100,000 units of the base currency):
Pip Value = (One Pip / Exchange Rate) × Lot Size - For a Micro Lot (10,000 units of the base currency):
Pip Value = (One Pip / Exchange Rate) × Lot Size - For a Nano Lot (1,000 units of the base currency):
Pip Value = (One Pip / Exchange Rate) × Lot Size
Example: For EUR/USD with an exchange rate of 1.1050 and trading one standard lot in Forex:
Pip Value = (0.0001 / 1.1050) × 100,000 = $9.05
For USD/JPY with an exchange rate of 110.10 and trading one standard lot:
Pip Value = (0.01 / 110.10) × 100,000 = $9.08
Forex Pip in Trading
Understanding Forex pips is crucial for executing various trading strategies. Here are some common applications:
Spread: The spread is the difference between the bid and ask price of a currency pair, often quoted in pips.
- Example: If EUR/USD has a bid price of 1.1050 and an ask price of 1.1052, the spread is 2 pips.
Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Orders: Stop-loss and take-profit orders are set at a specific number of pips away from the entry price to manage risk and secure profits.
- Example: If you buy EUR/USD at 1.1050, you might set a stop-loss at 1.1030 (20 pips) and a take-profit at 1.1070 (20 pips).
Calculating Profit and Loss: Profit or loss in a trade is calculated by multiplying the number of pips gained or lost by the pip value and the trade size.
- Example: If you buy a standard lot of EUR/USD at 1.1050 and sell at 1.1070, you’ve gained 20 pips. With a pip value of $10, your profit would be 20 pips × $10 = $200.
In modern forex trading, brokers often quote prices with an additional decimal place, known as fractional pips or pipettes. For most currency pairs, a pipette is one-tenth of a pip.
Example: If EUR/USD moves from 1.10505 to 1.10506, this represents a movement of one pipette, or 0.1 pips.
Fractional pips allow for more precise pricing and can lead to tighter spreads, which can be beneficial for traders, especially those engaged in high-frequency or algorithmic trading.
Practical Applications of Pip in Forex
Let’s explore how forex pips are used in practical forex trading strategies:
Scalping
Scalping is a trading strategy that involves making multiple trades throughout the day to capture small price movements. Scalpers heavily rely on their understanding of pips to quickly calculate profit and loss.
Example: A scalper might aim for 5 to 10 Forex pips per trade and make dozens of trades each day.
Forex Pips in Day Trading
Day traders aim to profit from short-term price movements within a single trading day. They usually target larger pip movements compared to scalpers.
Example: A day trader might target 20-50 pips per trade.
Swing Trading
Swing traders hold positions for several days to weeks, targeting significant price movements. They use pips to set wider stop-loss and take-profit levels.
Example: A swing trader might target 100-300 pips per trade.
Position Trading
Position traders hold trades for months or even years, focusing on long-term trends. They use Forex pips to measure long-term profit and loss.
Example: A position trader might target 500-1000 pips or more over several months.
Pip in Forex and Risk Management
Effective risk management is crucial in forex trading, and pips play a central role in this process. Traders use pips to determine position size, calculate the risk-to-reward ratio, and set stop-loss and take-profit levels.
- Calculating Position Size: Determining the correct position size helps manage risk. Traders often use a percentage of their account balance to calculate position size. For example, if you have a $10,000 account and risk 1% per trade, you are risking $100. If your stop-loss is 20 pips, your position size would be ($100 / 20 pips) = $5 per pip.
- Risk-to-Reward Ratio: The risk-to-reward ratio helps traders assess the potential profitability of a trade relative to its risk. A common ratio is 1:2, meaning you risk 1 pip in forex to gain 2 pips. For example, if you risk 20 pips for a potential reward of 40 pips, your risk-to-reward ratio is 1:2.
- Setting Stop-Loss and Take-Profit Levels: Stop-loss and take-profit orders are crucial for managing risk and locking in profits. Traders set these levels based on the number of pips they are willing to risk or aim for. For example, if you enter a trade at 1.1050, you might set a stop-loss at 1.1030 (20 pips) and a take-profit at 1.1070 (20 pips).
Conclusion
Understanding pip in forex is fundamental for trading. Pips quantify price movements and allow traders to measure profits and losses, calculate position size, set stop-loss and take-profit orders, and develop effective technical analysis strategies. Mastering pips and their practical applications can significantly enhance a trader’s ability to navigate the dynamic forex market.
Whether you’re a beginner or an experienced trader, a thorough understanding of forex pips enables you to make informed decisions, manage risk effectively, and achieve your trading goals. As you delve deeper into forex trading, the concept of pips will become an integral part of your trading toolkit, guiding you towards more precise and profitable trading outcomes.