What is Forex Oscillator? Oscillator vs Indicator
Forex Trading requires a deep understanding of technical analysis tools and strategies for making informed decisions. Among the numerous tools that traders use to analyze price movements and market trends, oscillators hold a special place.
They are often confused with indicators, but while all oscillators are indicators, not all indicators are oscillators. In this comprehensive guide by Omega Finex Broker, we will explain what an oscillator is, examine the difference between oscillator and indicator, and show how traders use them to enhance their trading strategies.**
What is an Forex Oscillator?
A Forex Oscillator is a type of technical analysis tool that fluctuates between two extreme values to identify overbought or oversold conditions in the market. Oscillators are generally used when the market is moving sideways or trading within a range.
They are especially useful in non-trending markets to show potential reversal points, giving traders clues about possible market reversals or entry and exit points. But why are they called oscillators?
The term “Forex Oscillator” comes from the way the tool moves back and forth between upper and lower bounds, usually between values like 0 and 100 or -1 and 1, depending on the type of oscillator. This distinction is what separates oscillators from other indicators. Oscillators can help traders answer the following questions:
- Is the market overbought or oversold?
- Are there signs of divergence between price movements and the oscillator, indicating a potential trend reversal?
- When is the best time to enter or exit a trade?
Key Forex Oscillators in Trading
There are several popular oscillators that traders often use. Let’s introduce some of the most common types of oscillators in Forex:
Relative Strength Index (RSI): RSI measures the speed and change of price movements, oscillating between 0 and 100. It is often used to identify overbought and oversold conditions. An RSI above 70 suggests that the asset is overbought, while a reading below 30 indicates it may be oversold.
Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD): Although not a pure oscillator, MACD can be used as an Forex Oscillator to measure momentum. It consists of two moving averages and a histogram. When the MACD line crosses above the signal line, it is a bullish signal; when it crosses below, it is bearish.
Stochastic Oscillator: The stochastic oscillator compares a currency pairs closing price to its price range over a specific period. It consists of two lines, %K and %D, which oscillate between 0 and 100. Readings above 80 are considered overbought, and readings below 20 are considered oversold.
Commodity Channel Index (CCI): CCI measures how far the price is from its average over a given period, oscillating between +100 and -100. Readings above +100 indicate overbought conditions, while readings below -100 indicate oversold conditions.
Awesome Oscillator (AO): This Forex Oscillator compares recent market momentum with overall momentum on a larger time frame. It is based on the difference between two simple moving averages.
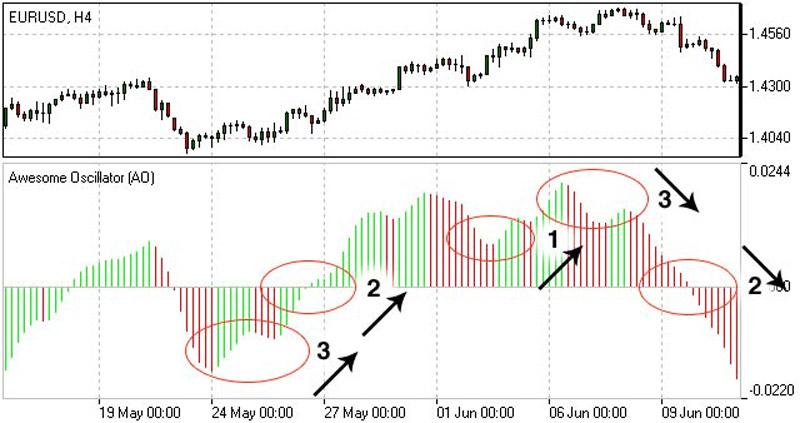
How Do Different Types of Oscillators Work in Forex?
Different types of oscillators in Forex operate within a set range and give traders insights into current market conditions. Most oscillators are designed to highlight when the market is either overstretched or compressed. They are particularly useful for identifying:
- Overbought and Oversold Conditions: When a Forex Oscillator has the upper limit of its range, the market is considered overbought. Conversely, when it reaches the lower limit, it is seen as oversold. Overbought conditions may indicate that a downward correction is likely, while oversold conditions suggest that an upward movement is imminent.
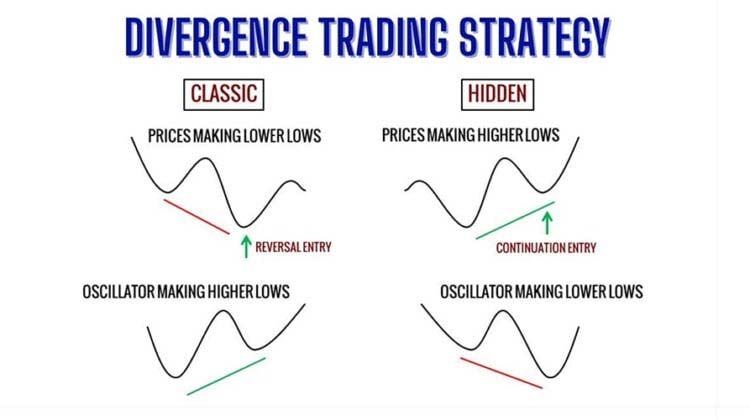
- Divergence: Divergence occurs when the price movement of a currency pair differs from the movement of the Forex Oscillator. For example, if the price is reaching a higher high, but the oscillator is making a lower high, this is known as “bearish divergence” and may indicate a potential market reversal. Conversely, “bullish divergence” occurs when the price and oscillator behave oppositely.
- Momentum: Forex Oscillators also measure the momentum of price movement for currency pairs. If the oscillator is rising, momentum is increasing, which could indicate a continuation of the current trend. Conversely, if it is decreasing, momentum is slowing, which may suggest a potential trend reversal.
What is the difference between oscillator and indicator?
One of the most common misconceptions in trading is the confusion between oscillators and indicators. While oscillators are a type of indicator, not all indicators are oscillators. Understanding the difference between oscillator and indicator is crucial for effective trading.
Indicators are mathematical calculations based on the price, volume, or open interest of a Forex pair. These calculations provide insights into the current market conditions and help traders make decisions based on historical data. Indicators can be categorized into two main types:
- Lagging Indicators: These indicators provide signals based on past price movements, making their response to current price action slower. Examples include moving averages and MACD.
- Leading Indicators: Leading indicators attempt to predict future price movements by analyzing current market conditions. Oscillators fall into this category, as they can often signal reversals before they occur.
Forex Oscillators, as mentioned, are a subset of leading indicators. They focus on showing the momentum and strength of price movement, especially in range-bound markets. Oscillators generally work best in markets without a clear trend and when a trader is looking for potential reversal points. This is the primary difference between oscillator and indicator in trading. The differences between oscillators and indicators can be summarized as follows:
Range Limits: The main difference between oscillator and indicators in Forex is the range within which they operate. Oscillators move within predefined limits (e.g., 0-100 or -100 to +100), whereas many other indicators have no set boundaries and can increase or decrease indefinitely.
Purpose: Oscillators are primarily used to determine momentum and overbought/oversold conditions, while other indicators, like trend indicators (such as moving averages), are used to confirm trend direction. This is another distinction between oscillators and indicators in trading.
Application: Forex Oscillators are more effective in range-bound or non-trending markets, whereas other indicators, such as lagging indicators, are more effective in trending markets. Understanding these applications is key to choosing the right tool.
Using Forex Oscillators in Trading Strategies
When used correctly, oscillators are powerful tools. Here are some common strategies traders employ using Forex oscillators:
Overbought/Oversold Strategy
When an Forex Oscillator signals overbought conditions (e.g., RSI above 70), traders may look for selling opportunities. Conversely, when the oscillator shows oversold conditions (e.g., RSI below 30), traders may look for buying opportunities.
Divergence Strategy for Forex Oscillator in trading
Traders often use divergence between price and the oscillator to anticipate reversals. For example, if the price is rising but the oscillator is falling, this could be an early signal of a bearish reversal.
Combining Oscillators with Trend Indicators to Benefit from Their Differences
Many traders combine oscillators with other indicators to confirm signals. For example, a trader might use a moving average to identify the trend direction and an Forex Oscillator to find the best entry point. If the trend is upward, they may wait for the oscillator to show oversold conditions before entering a buy position.
Common Mistakes and Issues with Forex Oscillators
Despite their usefulness, oscillators are not error-proof. Traders should be aware of some common issues:
- Ignoring the Trend: Forex Oscillators can give false signals in a strongly trending market. For example, during a strong uptrend, RSI might indicate overbought conditions, yet the market continues to rise. Relying solely on an oscillator in such cases can lead to premature exits or missed opportunities.
- Relying on a Single Oscillator: Some traders rely exclusively on one Forex Oscillator for their trading decisions, which can lead to poor outcomes. Using oscillators alongside other indicators and tools is crucial for gaining a complete view of the market.
- Overtrading: Forex Oscillators can generate frequent signals, which may tempt traders to overtrade. Maintaining a disciplined approach and only trading when the oscillator aligns with other technical or fundamental analysis is essential.
Summary
Forex Oscillators are essential tools in traders’ arsenals, especially in range-bound markets. By providing insights into overbought and oversold conditions, measuring momentum, and identifying divergence, oscillators can help traders time their entries and exits more effectively.
However, like any tool, oscillators should not be used in isolation. Combining them with other indicators and market analysis creates a more balanced trading strategy.
In short, the difference between oscillator and indicators is that oscillators in Forex are a specialized subset of indicators focused on identifying momentum and potential reversals. Their primary function is to highlight when the market is overbought or oversold and likely to reverse, making them valuable in range-bound conditions. With proper understanding and application, oscillators can significantly improve a trader’s ability to navigate Forex markets successfully.